Table of Contents
Introduction to Moral Suasion
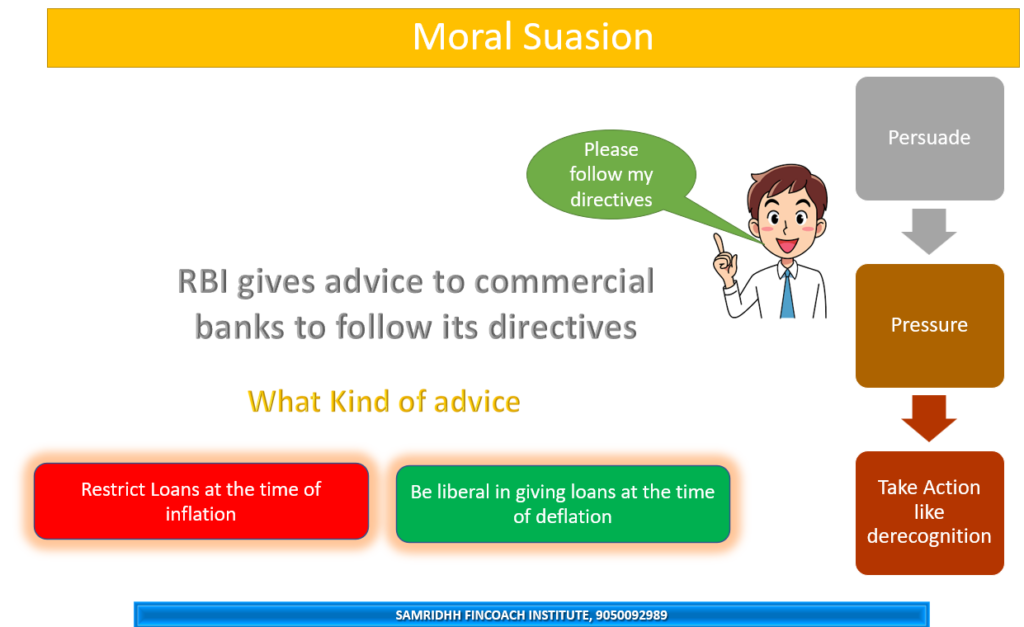
Moral suasion as a qualitative instrument of credit control is a method used by the central bank to influence the lending behaviour of commercial banks and other financial institutions by using its moral authority and persuasive power, rather than legal or regulatory means. Moral suasion involves the central bank issuing advice, suggestions, requests and appeals to the commercial banks to cooperate with its monetary policy objectives and to follow certain norms and guidelines in their credit operations.
Unlike quantitative tools that directly regulate the volume of credit through statutory requirements, moral suasion relies on the voluntary cooperation of financial institutions. This approach leverages the central bank's authority and relies on the reputational consequences on commercial banks that might follow if banks choose not to comply.
This is the first line of action taken by the central bank when it observes some unwanted behaviour at the end of commercial banks or anywhere else in the banking system
Goals of Moral Suasion
Moral suasion can be used by the central bank to achieve various economic and financial objectives:
- To restrain or expand the overall credit creation in the economy, depending on the economic conditions and the inflation or deflation situation.
- To direct the credit flow to certain priority sectors or industries that are considered socially or economically desirable, and to discourage the credit flow to certain non-priority or speculative sectors or industries that are considered harmful or risky.
- To maintain the stability and soundness of the banking system and to prevent any financial crisis or contagion.
- To enhance the confidence and trust of the public and the market participants in the central bank's policies and actions.
Application Methods
Moral suasion can be applied in public as well as in private. The central bank employs various channels of communication to convey its expectations:
Public Methods
- Public statements
- Speeches by officials
- Press releases
- Reports and publications
- Central bank website announcements
Private Methods
- Private meetings
- One-on-one discussions
- Official letters
- Phone calls
- Advisory notices
It's important to note that moral suasion is not a statutory obligation or a legal compulsion for the commercial banks. It is based on the voluntary cooperation and compliance of the commercial banks with the central bank's wishes.
Effectiveness Factors
The effectiveness of moral suasion depends on various factors that influence how commercial banks respond to central bank guidance:
Credibility & Reputation
The credibility and reputation of the central bank as a monetary authority and a regulator.
Interest Alignment
The degree of alignment or divergence between the central bank's objectives and the commercial banks' interests and incentives.
Implicit Consequences
The presence or absence of implicit or explicit threats or rewards by the central bank for following or not following its moral suasion.
Alternative Sources
The availability or unavailability of alternative sources of funds or markets for the commercial banks.
Market Competition
The level of competition or cooperation among the commercial banks.
Real-World Examples
Here are some examples of how moral suasion has been used by central banks as a qualitative instrument of credit control:
Historical Example: National Credit Plan
In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has used moral suasion extensively to regulate the credit creation and allocation by commercial banks. One of the areas where the RBI used moral suasion to a significant extent was in the implementation of the National Credit Plan (NCP) under which the Banks' annual monetary program was combined with a diversion of commercial bank credit to pre-determined priority areas.
Recent Examples of RBI's Moral Suasion
Paytm Payments Bank (2024)
After identifying persistent non-compliance issues at Paytm Payments Bank, rather than immediately imposing severe sanctions, the RBI first used moral suasion through private communications and meetings with the management. When compliance issues persisted, the RBI imposed business restrictions in January 2024, directing the bank to stop accepting new deposits and conducting credit transactions. This approach gave Paytm time to address regulatory concerns before more formal actions were taken.
Unsecured Lending Concerns (2023)
In 2023, the RBI used public speeches and banking conference addresses to caution banks about the rapid growth in unsecured loans and co-lending arrangements with non-banking financial companies (NBFCs). Rather than immediately increasing risk weights on such loans, the RBI first tried to persuade banks to voluntarily moderate their unsecured lending. When the moral suasion was insufficient, the RBI later increased risk weights on unsecured personal loans and credit card receivables.
Cryptocurrency Trading (2022-2023)
Before establishing formal regulations, the RBI used moral suasion through public statements cautioning banks against facilitating cryptocurrency transactions. The central bank held private discussions with banking leaders and issued informal advisories about the risks associated with crypto assets, encouraging banks to exercise extreme caution in this domain while the regulatory framework was being developed.