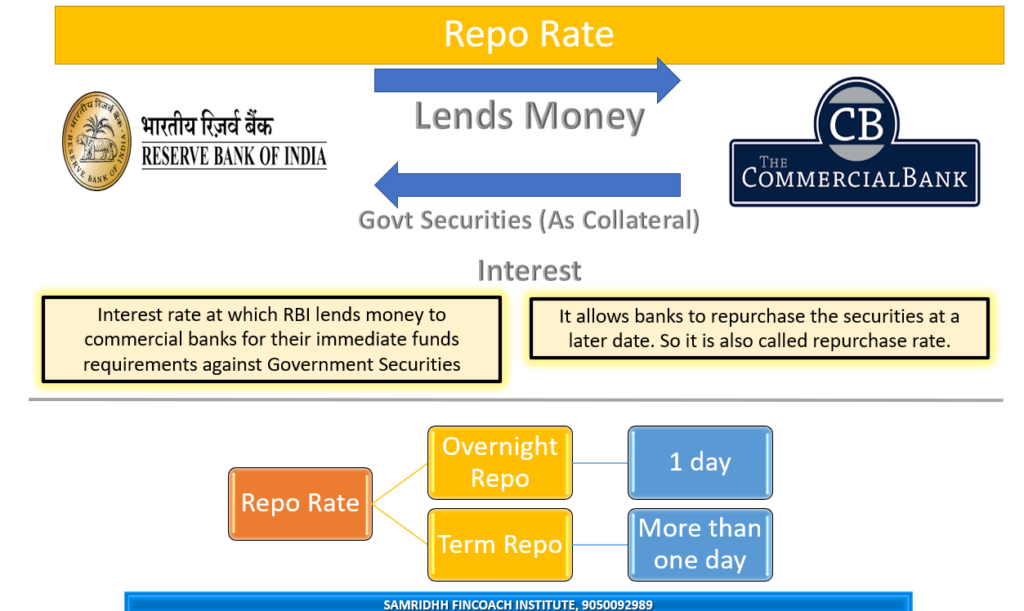
Repo rate is the interest rate that the central bank of a country charges from the commercial banks when they borrow money from it. Repo rate is also called repurchase rate, which means that the commercial banks have to repurchase or buy back the securities that they sell to the central bank as collateral for the loan. Repo rate is one of the tools that the central bank of the country uses to control the money supply, inflation, and economic growth in the country.
Suppose you are a commercial bank and you need some money to lend to your customers or to meet your daily obligations. You can borrow money from the central bank by selling some of your government securities, such as treasury bills or bonds, to it. The central bank will lend you money at a certain interest rate, which is called the repo rate. You also agree to buy back those securities from the central bank at a later date, usually within a few days or weeks. The difference between the price at which you sell and buy back the securities is the interest that you pay to the central bank.
For example, suppose you sell securities worth Rs. 100 crore to the central bank and borrow money from it at a repo rate of 6%. You agree to repurchase those securities after 7 days. This means that after 7 days, you have to pay back Rs. 100.1 crore to the central bank (Rs. 100 crore plus Rs. 0.1 crore as interest). The interest amount is calculated as follows:
Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
Interest = Rs. 100 crore x 6% x 7/365
Interest = Rs. 0.1 crore
Now, suppose the central bank changes the repo rate from 6% to 7%. This means that if you borrow money from the central bank again by selling securities worth Rs. 100 crore, you have to pay back Rs. 100.13 crore after 7 days (Rs. 100 crore plus Rs. 0.13 crore as interest). The interest amount is calculated as follows:
Interest = Rs. 100 crore x 7% x 7/365
Interest = Rs. 0.13 crore
As you can see, when the repo rate increases, you have to pay more interest to the central bank for borrowing money from it. This makes borrowing money from the central bank more expensive and less attractive for you. You may decide to borrow less money from the central bank and lend less money to your customers or charge higher interest rates to them. This reduces the money supply and credit availability in the economy and helps to control inflation and excessive demand.
On the other hand, when the repo rate decreases, you have to pay less interest to the central bank for borrowing money from it. This makes borrowing money from the central bank cheaper and more attractive for you. You may decide to borrow more money from the central bank and lend more money to your customers or charge lower interest rates to them. This increases the money supply and credit availability in the economy and helps to stimulate economic activity and growth.
The repo rate also affects other interest rates in the economy, such as deposit rates, loan rates, bond yields, etc., as they are influenced by the cost of borrowing from the central bank.
Owner Contact me on : contact.tejasji@gmail.com