What is Fiscal Policy
It refers to revenue and expenditure policy of the government.
To Correct the problems of Deficient demand and Excess Demand following four components of fiscal policy are used :
- Government Expenditure
- Government receipts (Taxes)
- Public Debt
- Borrowings from RBI
Components of Aggregate Demand
In this context it is pertinent to recap the four components of Aggregate Demand
- Household Consumption Expenditure
- Private Investment Expenditure
- Government Expenditure (Both consumption and investment). It covers construction of roads, dams, education and public welfare programs, defense expenditure, etc.
- Net Exports (Exports - Imports)
To correct the problem of excess demand any or all of the above should be reduced through policy measures. Similarly for correcting the problem of deficient demand any or all of the above should be increased through policy measures
Government Expenditure
To Correct Deficient Demand - Government expenditure is increased. This directly generates additional demand in the economy and also releases more liquidity into the economy.
To Correct Excess Demand - Government expenditure is decreased. This cuts aggregate demand in the economy and also absorbs excess liquidity from the economy.

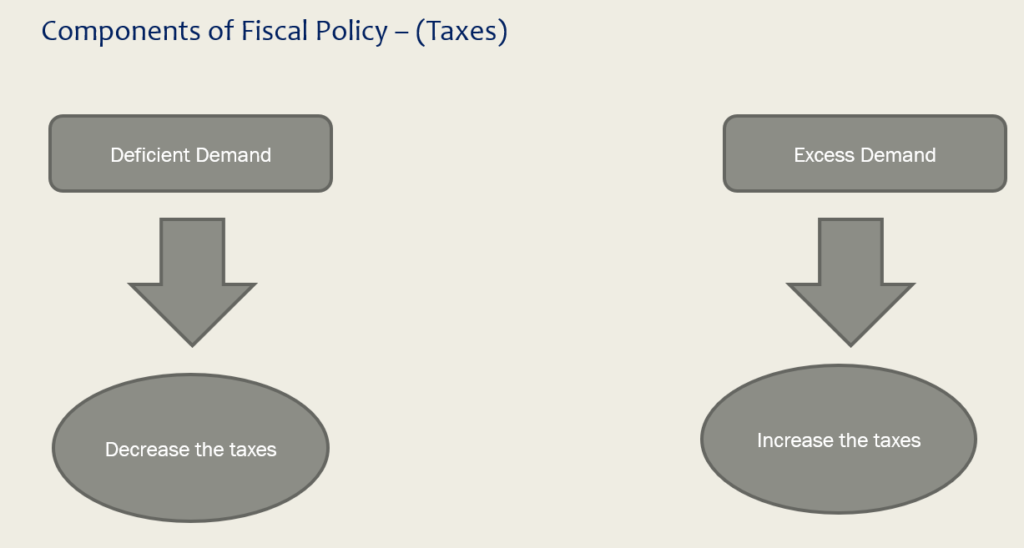
Government Receipts (Taxes)
There are two types of taxes : a) Direct Taxes like Income Tax b) Indirect Taxes like Goods and Services tax
Both the above types of taxes helps in controlling aggregate demand in the economy
Direct Taxes
To Control Deficient Demand : If the direct taxes like income tax is reduced then it leaves more disposal income into the hands of people which results into higher demand for goods and services. Example Suppose Income is Rs 100. Income tax rate is 20%. In this case Disposable income will be (Rs 100 - Rs 20 = Rs 80). Now if the government decreases the income tax rate to 10%. In this case Disposable income will be (Rs 100 - Rs 10 = Rs 90). So the impact of decreasing the direct tax is increasing the disposable income and hence the demand for goods and services
To Control Excess Demand : Direct Taxes are increased so that the disposable income is reduced
Indirect Taxes
To Control Deficient Demand : Indirect taxes will be decreased. This will bring fall in prices and hence will increase demand for goods and services
To Control Excess Demand : Indirect taxes will be increased. This will bring rise in prices and hence will decrease demand for goods and services
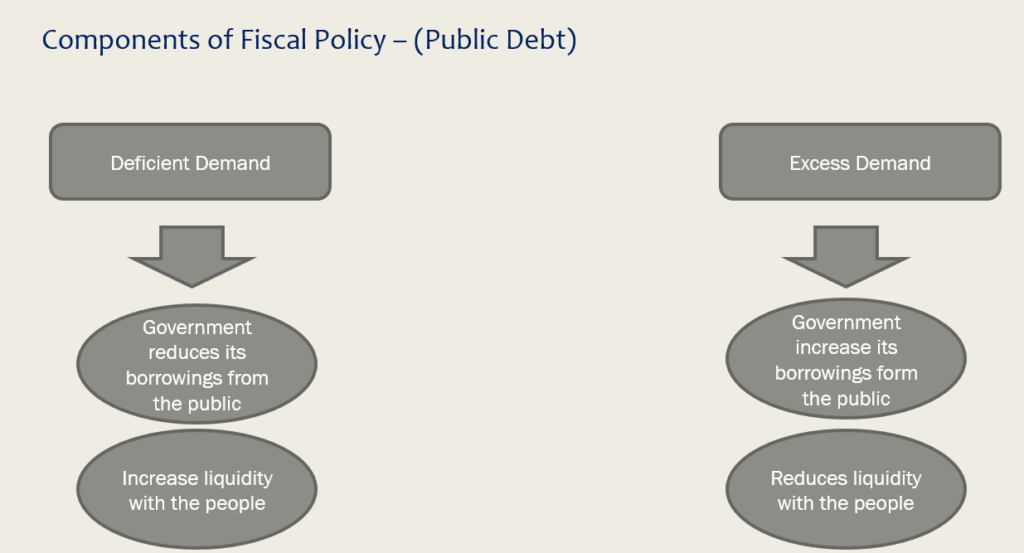
Public Debt
This refers to the borrowings that the government does from the people of the country to meet its finances.
To Control Deficient Demand : Borrowings from the public are decreased. This leaves more money in the hands of the people. Thus they demand more goods and services, resulting into higher aggregate demand in the economy.
To Control Excess Demand : Borrowings from the public are increased. This leaves less money in the hands of the people. Thus they demand less goods and services, resulting into lower aggregate demand in the economy.
Government Borrowings from Central Bank (RBI)
To Control Deficient Demand : Government will increase its borrowings from central bank so as to release higher liquidity into the economy. More money will chase more goods and services resulting into increase in aggregate demand
To Control Excess Demand : Government will decrease its borrowings from central bank so as to release lesser liquidity into the economy. Less money in the economy will bring in reduction in aggregate demand.
